|
|||||
|
|
WHAT ARE THE MAIN
FEATURES OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM? |
||||
|
|||||
|
|
WHAT ARE THE MAIN
FEATURES OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM? |
||||
| The main features of the porcine immune system are: | |||
|
| 1.- The capability of discriminating between
its own and foreign
components.
The immune system has the capability of discriminating between self and foreign components, by reacting against everything different to itself (Antigens). The immune system has the amazing characteristic of reacting against any foreign molecule, different to its own structure, no matter how small this molecule is. However, it does not react against its own structures. This characteristic is one of the most important principles of immunology. During the embryonic stage, the lymphocytes that recognize their own structures are eliminated, by means of an apoptosis process, (programmed cell death). Only the cell clones that react against foreign structures will pass into circulation, whenever they are associated to the own SLA, as well as the clones tolerant to the self structures. The histocompatibility antigens (SLA) play a main role in this selection. Sometimes, the immune system may be mistaken when discerning self and foreign components. Thus, it is possible that the immune system does not react against a foreign particle. This phenomenon is called tolerance. On the other hand, the immune system can react against its own structures. These reactions are called autoimmunity. In the thymus, lymphocytes are selected in such a way that they can only react against the foreign particles (positive selection). Only these lymphocytes will go into blood circulation. In addition,, cellular destruction (apoptosis) of the lymphocytes that react against the self structures is produced. |
2.- Specificity. The specificity of the immune system is due to the fact that both lymphocytes and antibodies only recognize one epitope or antigenic determinant. The immune system can recognize thousands of millions of different antigens, but for each determinant, a specific lymphocyte will be induced. There are as many stimulated lymphocytes as determinants forming the antigen. 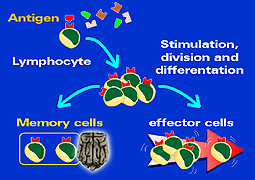
Specific recognition of a single
antigenic determinant (one determinant = one cell). After the recognition, a
proliferation of cells takes place.Because of this the lymphocytes become part of the memory lymphocytes, and others will
act as effector cells. |
|
| 3.- Memory
|
||
|
|||||