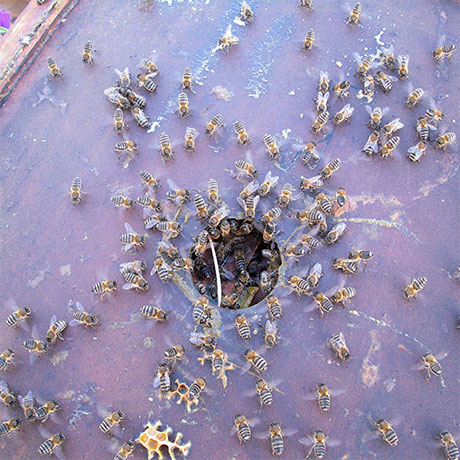
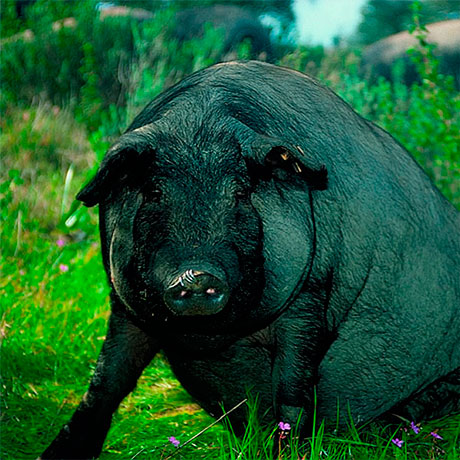
Estudio de la interacción entre cerdos criados en libertad y jabalíes en un área endémica de peste porcina africana

Nuevo artículo publicado en la revista Frontiers in Veterinary Science.
Resumen:
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is spreading throughout Eurasia and there is no vaccine nor treatment available, so the control is based on the implementation of strict sanitary measures. These measures include depopulation of infected and in-contact animals and export restrictions, which can lead to important economic losses, making currently African swine fever (ASF) the greatest threat to the global swine industry. ASF has been endemic on the island of Sardinia since 1978, the longest persistence of anywhere in Eurasia. In Sardinia, eradication programs have failed, in large part due to the lack of farm professionalism, the high density of wild boar and the presence of non-registered domestic pigs (free-ranging pigs).
El papel del jabalí en la propagación de la Peste Porcina Clásica en Japón
 Nueva publicación en la revista Pathogens.
Nueva publicación en la revista Pathogens.
Resumen en inglés:
Since September 2018, nearly 900 notifications of classical swine fever (CSF) have been reported in Gifu Prefecture (Japan) affecting domestic pig and wild boar by the end of August 2019. To determine the epidemiological characteristics of its spread, a spatio-temporal analysis was performed using actual field data on the current epidemic. The spatial study, based on standard deviational ellipses of official CSF notifications, showed that the disease likely spread to the northeast part of the prefecture. A maximum significant spatial association estimated between CSF notifications was 23 km by the multi-distance spatial cluster analysis. A space-time permutation analysis identified two significant clusters with an approximate radius of 12 and 20 km and 124 and 98 days of duration, respectively. When the area of the identified clusters was overlaid on a map of habitat quality, approximately 82% and 75% of CSF notifications, respectively, were found in areas with potential contact between pigs and wild boar. The obtained results provide information on the current CSF epidemic, which is mainly driven by wild boar cases with sporadic outbreaks on domestic pig farms. These findings will help implement control measures in Gifu Prefecture.
Ito S., Jurado C., Bosch J., Ito M., Sánchez-Vizcaíno JM., Isoda N. y Sakoda AY.
Vacunación oral en jabalíes silvestres: una nueva esperanza frente a la Peste Porcina Africana
Artículo de divulgación científica publicado en la revista porciNews (porcino.info)
 La Peste Porcina Africana (PPA), la mayor amenaza para el sector porcino de todo el mundo, se ha propagado a más de 55 países en tres continentes estimándose una afectación de más del 77% de la población porcina mundial. La Peste Porcina Africana es una de las enfermedades víricas de mayor impacto en el sector porcino, ya que las cepas virueltnas del virus provocan fiebre hemorrágica aguda o hiperaguda en los animales con una mortalidad de hasta el 100%. Debido a sus devastadoras consecuencias socioeconómicas y sobre la salud animal, la PPA está catalogada como una Enfermedad de Declaración Obligatoria a la OIE.
La Peste Porcina Africana (PPA), la mayor amenaza para el sector porcino de todo el mundo, se ha propagado a más de 55 países en tres continentes estimándose una afectación de más del 77% de la población porcina mundial. La Peste Porcina Africana es una de las enfermedades víricas de mayor impacto en el sector porcino, ya que las cepas virueltnas del virus provocan fiebre hemorrágica aguda o hiperaguda en los animales con una mortalidad de hasta el 100%. Debido a sus devastadoras consecuencias socioeconómicas y sobre la salud animal, la PPA está catalogada como una Enfermedad de Declaración Obligatoria a la OIE.
Entrevista del profesor Sánchez-Vizcaíno para la televisión Sur Koreana
Nuevo artículo publicado en la revista Scientific Records de Nature research
 Título: Risk of African swine fever virus introduction into the United States through smuggling of pork in air passenger luggage
Título: Risk of African swine fever virus introduction into the United States through smuggling of pork in air passenger luggage
Resumen (inglés)
African swine fever causes substantial economic losses in the swine industry in affected countries. Traditionally confined to Africa with only occasional incursions into other regions, ASF began spreading into Caucasian countries and Eastern Europe in 2007, followed by Western Europe and Asia in 2018. Such a dramatic change in the global epidemiology of ASF has resulted in concerns that the disease may continue to spread into disease-free regions such as the US. In this study, we estimated the risk of introduction of ASF virus into the US through smuggling of pork in air passenger luggage. Results suggest that the mean risk of ASFV introduction into the US via this route has increased by 183.33% from the risk estimated before the disease had spread into Western Europe or Asia. Most of the risk (67.68%) was associated with flights originating from China and Hong Kong, followed by the Russian Federation (26.92%). Five US airports accounted for >90% of the risk. Results here will help to inform decisions related to the design of ASF virus surveillance strategies in the US.
Jurado C., Mur L., Perez-Aguirreburualde MS., Cadenas-Fernández E., Martínez-López B., Sánchez-Vizcaíno JM y Pérez A.